Principles of inheritance and variations class 12 MCQs term 1 pdf download
MCQ TYPE QUESTIONS :-
1. Who rediscovered the mendel's work:-
a. Correns
b. Hugo de Vries
c. Tschermak
d. All of the above
2. In which year the mendel‘s work has been published:-
a. 1864
b.1865
c.1866
d.1867
3. Who has given the concept of gene mapping:-
a. Morgan
b.Gregor John Mendel
c.Alfred Sturtevant
d. Henking
4. Male heterogametic condition found in :-
a. Humanbeing
b. Fowl
c. Both A & B
d. Not certain
5. Who invented X chromosomes:-
a. MacClintok
b. Johenson
c. Morgan
d. Henking
6. Trisomy found in:-
a.Turner‘s Syndrome
b. Klinefelter‘s syndrome
c. Down‘s Syndrome
d. All of the above
7. Failure of which stage of cytokinesis cause polyploidy:-
a. Prophase
b. Metaphase
c. Anaphase
d. Telophase
8. In phenylketonuria the amino acid phenylalanine fails to convert in which amino acid:-
a. Serine
b. Tyrosine
c. Glutamic Acid
d. Valine
9. In Sickle cell anemia , at which position , the amino acid get changed:-
a. Fourth position
b. Fifth position
c. Sixth position
d. Seventh position
10. If the diploid number of chromosomes are 32 in honey bees , then how many chromosomes found in the male honey bees or drones:-
a. 16
b. 32
c.48
d. 16 & 32 both
11. There is certain feminine features develop in an individual with XXY chromosomes configuration , then what is the suitable term can be given to the situation:-
a. Gynaecomastia
b. Gynaecophoria
c. Gynaecoinducia
d. Gynaecoblastia
12. Which of the following disease belong to autosomal recessive mendelian disorder:-
a. Colour blindness
b. Haemophilia
c. Sickle cell anaemia
d. All of the above
13. Incomplete Dominance , is the deviation of which law of Mendel:-
a. Law of dominance
b.Law of segregation
c.Law of independent assortment
d.All of the above
14. Pleiotropy , can be defined as:-
a. When one gene control one trait
b. When one gene exhibit multiple traits
c. When multiple genes control one trait
d. When multiple genes control multiple traits.
15. Polygenic inheritance can be observed in:-
a. In the eye colour of human being
b. In the skin colour of human being
c. In the hair colour pattern
d. All of the above
16. In fowl , which parent is responsible to determine the sex of offsprings :-
a. Male parent
b. Female parent
c. Both parents
d. By environment conditions
17. In pea plants ,the pod shape may be inflated or constricted , which traitis dominanttrait:-
a. Inflated
b. Constricted
c. Both of them
d. Not certain
18. What would be the phenotype of a plant that has genotype Tt :-
a. Tall
b. Dwarf
c. Semi dwarf
d. Not certain
19. Out of sperms and ova , which gamete is responsible to determine sex in chick :-
a. Sperm
b. Ovum
c. Both the gametes
d. Depend upon environment conditions
20. What will be the percentage of pea plants that would be homozygous recessive in the F2 generation , when tall F1 heterozygous pea plants are selfed :-
a. 25%
b. 50%
c. 75%
d. 100%
21. What percentage of homozygous and heterogeneous populations are produced in F2 generation in a mendelian monohybrid cross :-
a. 25%and25%
b. 50% and 50%
c. 25% and 75%
d. 25 % and 50%
22. Write the genotypes Mendel obtained , after the cross between f-1 violet flowered plants with white flowered pea plant:-
a. VV & vv
b. VV&Vv
c. Vv&Vv
d. Vv &vv
23. Which law of Mendel , has universally accepted
a. Law of dominance
b. Law of segregation
c. Law of independent assortment
d. None of these
24. RrYy has been crossed with rryy. Give a suitable term of the cross:-
a. Monohybrid cross
b. Test cross
c. Back cross
d. Self cross
25. How many alleles are responsible to determine the skin colour of human being:-
a. 2pairs
b. 3 pairs
c. 4 pairs
d. 5 pairs
26. In a population of Drosophila, 25% offsprings are similar to their parents , reason behind this similarly is :-
a. Recombination
b. Linkage
c. Variation
d. All of the above
27. In human being , the 2n=46, how many linkage groups are found on it :-
a. 23
b. 46
c. 23 pairs
d. 46 pairs
28. In the male gamete of an organism 8 chromosomes are found .Out of which one is X chromosome. how many autosomes will be found in the gamete:-
a. 7
b. 8
c. 14
d. 16
29. Male honey bees produced by parthenogenesis ,which type of cell division found during Gametogenesis of such male bees:-
a. Mitosis
b. Meiosis
c. Amitosis
d. All of the above
30. Which of the following is x linked recessive disease:-
a. Sickle cell anemia
b.Thalassemia
c. Phenylketonuria
d. Haemophilia
31. Which of the following organism , has XO sex chromosome in male individuals:-
a. Human being
b. Fowl
c.Insects
d. None of the above
32. A human zygote has XXY sex chromosome along with 22 pairs of Autosome, what will be the sex of the individual the individual developing from the zygote:-
a. Male
b. Female
c. Both A & B
d. Not certain
33. There is a gene which is responsible to control the shape of the seeds and the size of the starch grains and the nature of protein coat around The Seed. Which type of gene it
would be:-
a. Polymorphic gene
b. Pleiotropic gene
c. Multiple genes
d. All of the above
34. What are the number of chromosomes, retain the genes for Alpha thalassemia and beta thalassemia respectively:-
a. 11 &16
b. 16&11
c. 16&20
d. 11 & 20
35. An individual human being has 45 chromosomes, which type of chromosomal disorders likely to occur:-
a.Down's syndrome
b. Turner's syndrome
c. Klinefelter syndrome
d. None of the above
36. A colour blind son born from normal parents, what would be the genotype of the maternal grandfather:-
a. XcY
b. XcYc
c.XY
d. None of the above
37. Mother‘s blood group is A and father‘s blood group is B and the daughter‘s blood group is O. What will be the blood group of other children:
a. A
b. B
c. AB
d. All of the above
38. What are the outcome of gene mapping:-
a. The chances of recombination
b. The chances of linkage
c. To locate at the proper locus of a gene
d. All of the above
39. Phenylalanine hydroxylase enzyme , responsible to convert :-
a. Phenylalanine to glutamic Acid
b. Phenylalanine to valine
c. Phenylalanine to tyrosine
d. Phenylalanine to glycine
40. What is the phenomenon that occurred in the failure of separation of homologous chromosomes , during meiosis:-
a. Non lsolation
b.Non distinction
c. Non disjunction
d. Non separation
41. The genotype of affected individual with sickle cell anemia will be:-
a. HbsHbs
b.HbsHba
c. HbaHba
d. HbaHbs
42. During sickle cell anemia , in what form does the replacement can be seen in codon :-
a. GAGto GTG
b. GAGtoGUG
c. GAGtoGCG
d. GAG to CAG
43. A haemophilic son born to normal parents. Give the genotype of parents:-
a. Mother XX father XCY
b. Mother XhX , father XY
c. Mother XX, father XY
d. None of the above
44. Which of the following is not a wild type phenotype in drosophila:-
a. Miniature wings
b. White eye
c. White body
d. Normal wing
45. How many contrasting characters are found in the pea plants:-
a. 5 pairs
b. 6 pairs
c. 7 pairs
d. 8 pairs
46. In which year chromosomal theory of inheritance was postulated:-
a. 1900
b. 901
c. 1902
d. 1903
47. How does mendelian disorders caused:-
a. Due to defected autosomal gene
b. Due to defected X linked gene
c. Due to defected autosomal as well as X linked gene
d. None of the above
48. In complete linkage, the off springs with recombination, in F2 generation are:-
a. 1.1%
b.1.2%
c. 1.3 %
d. 1.4%
49. In incomplete linkage , the offsprings with parental combination in F2 generation are:-
a. 68.2%
b. 62.8%
c.68.3%
d. 62.3 %
50. Two heterozygous parents are crossed. if two loci are linked what would be the distribution of phenotypic features in F1 generation for a dihybrid
cross:-
a. Complete linkage
b. Incomplete linkage
c. Partial complete linkage
d. Partial incomplete linkage
51. Multiple allelism is the concept which tells us :-
B) One gene control several traits
C) Several genes control one treat
D) One gene control one trait
E) Several genes control several traits
52. Which example is given by ABO blood group pattern:-
B) Codominance
C) Incomplete dominance
D) Polygenic inheritance
E) Multiple allelism
53. In a monohybrid cross in F2 generation 64 dwarf plants have been produced. how many hybrid tall plants will be produced in the same cross:-
a) 64
b. 128
c.192
d. 256
54. Why the traits of plants in F2 generation of mendelian monohybrid cross , not blended :-
B) Because the factors are located at different loci
C) Because due to no crossing over
D) Because factors are found on different chromosomes
E) All of the above
CRITICAL & CREATIVE THINKING QUESTIONS:-
The chances of colour blindness about 8 % of males and only about .4 % of females. This is because the genes that lead to red green colour blindness are on the X
chromosome. Males have only one X chromosome and females have 2. Another sex linked recessive disease, which shows its transmission from unaffected carrier female to
some of the male progeny has been widely studied. In this disease a single protein that is a part of the cascade of proteins involved in the clotting of the blood is affected. Due to this in an
affected individual a simple cut will result in nonstop bleeding. The heterozygous female (carrier) for haemophilia may transmit the disease to sons. The possibility of a female
becoming a haemophilic is extremely rare because mother of such a female has to be at least carrier and the father should be haemophilic.
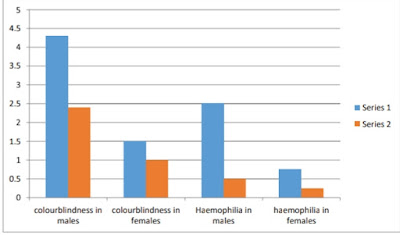
Note :- in each group bar 1 represent the individuals of less than 12 years of age. And bar 2 represent the individuals of more than 12 years of age.
GRAPH : DEPICTS THE VIABILITY OF INDIVIDUALS WITH X LINKED MENDELIAN DISORDERS
1. The reason for low viability of human females with haemophilia is :-
a. Non clotting of the blood
b. Loss of major volume of blood during menstruation.
c. Lack of the coagulating protein
d. All of the above.
2. What is the reason of the drastic loss of viability of affected males with haemophilia :-
a. Low volume of blood b. Lack of the clotting protein
c. Less platelet count d. All of the above.
3. Which protein is responsible for coagulation of blood :-
a. Fibrin b.Albumin c. Globulin d. None of the above
4. Why the colour blindness is more common in male than females :-
a. It is caused by a recessive gene.
b. It is located on X chromosome.
c. Female can be of heterozygous genotype.
d. All of the above.
5. Howcarriermothermaynotinherit colour blindness toheroffsprings :-
a. Affected gene is only found on one X chromosome.
b. Mother may inherit normal X chromosome to the new generation.
c. Offsprings will be heterozygous genotype.
d. All of the above.
CASE BASE STUDY QUESTIONS: - MENDELIAN DISORDERS
Broadly, genetic disorders may be grouped into two categories – Mendelian disorders and Chromosomal disorders. Mendelian disorders are mainly determined by alteration
or mutation in the single gene. These disorders are transmitted to the offspring on the same lines as we have studied in the principles of inheritance. Most common and prevalent
Mendelian disorders are Haemophilia , Cystic fibrosis , Sickle cell anemia, Colour blindness , Phenylketonuria , Thalassemia. The Mendelian disorders may be recessive or dominant.
Similarly the trait may also be linked to the case of sex chromosome like haemophilia. It is evident that this X – linked recessive trait shows transmission from carrier female
to male progeny. A Mendelian disorder caused if the mutated gene is found either in homozygous or in heterozygous forms. A recessive disease only expressed in the homozygous
genotype , whereas the dominant diseases expressed in heterozygous genotype also. The defected gene may be found on to the autosome, like in thalassemia, the alpha type , gene is
found on chromosome number 16 and beta type the gene is found on chromosome number 11. On the other hand when the defected gene is on X chromosome , then it will be considered as X linked diseases. Father never transmit or inherit the X linked diseases to the son , because from father―Y‖ chromosome get inherited to his son and this chromosome not has any gene of the diseases.
1. Which disease is not Mendelian Disease :-
a. Down‘s Syndrome
b. Sickle cell Anemia
c. Thalassemia
d. Phenylketonuria
2. A female with gene of colour blindness may be normal , because :-
a. One X chromosome has the defected /mutated gene
b. Both X chromosomes have defected/mutated gene.
c. Y chromosome has the defected/muted gene.
d. Both A & B
3. A son not getting X linked Mendelian disease from affected father because :-
a. The gene is located on X chromosome.
b. Father inherit Y chromosome to his son.
c. X chromosome is inherited to the daughter.
d. All of the above
4. Sickle cell Anemia and thalassemia are different from each other :-
a. They created by autosomal genes.
b. They are related to the disorder of blood.
c. They are autosomal recessivediseases.
d. Sickle cell anemia is qualitative and thalassemia is quantitative diseases.
5. Which two colours can not be identified in the colour blindness :-
a. Blue & green b. Red & green c. Red & blue d.Violet & blue
CASE BASED STUDY QUESTIONS :- PARTHENOGENESIS
In the population of honey bees, the male honey bees develop from unfertilized ovum, and the number of chromosomes found in the male bees are 16. The male honey bees are also
called as drones. And they have half number of the chromosomes with respect to the females. Male bees are haploid and female bees are diploid. Female bees have 32 chromosomes. During Gametogenesis male bees perform mitosis , whereas the female bees perform meiosis. If we study the making of progeny among the honey bees , we found that the female bees make both male and female , and the male bees only make females. That is why the male not have father as well as male bees not have son. Meanwhile the male honeybees have grandfather and grandson as well.
1. Why mitosis not applicable during
gametogenesis of female honeybees :
b. Female bees arediploid.
c. Female bees need to produce haploid offsprings.
d. Female bees need to produce male bees by parthenogenesis.
2. A male honey bee not has son because :-
a. The male gamete are not in proper number.
b. The male gametes are not used to make male offsprings
c. The male gametes are yet to be in diploid chromosome number.
d. The female gamete develop in to a male bee directly.
3. What is the number of chromosomes in the queen honey bee :-
a. 16 b. 32 c.48 d. Not certain
4. What is the role of the mitosis in the Gametogenesis in male honey bees :-
a. It maintains haploid number of chromosomes.
b. Since the male bees are haploid , so meiosis is not needed.
c. For the making of the diploid offsprings
d. All of the above.
CASE BASE STUDY QUESTIONS:-. CO-DOMINANCE
In the case of co-dominance, the f-1 generation resembles both parents. A good example is different types of red blood cells that determine ABO blood grouping in human being. ABO blood groups are controlled by the gene I. The plasma membrane of the red blood cells has sugar polymers that protrude from its surface and the kind of sugar is controlled by
the gene. The gene I has three alleles IA, IB and i. The alleles IAand IB produce a slightly different form of the sugar while allele it does not produce any sugar. Because humans
are diploid organisms, each person possesses any two of the three I gene alleles. IA and IB arecompletely dominant over I, in other words when IA and i are present, IA
expresses. (because it does notproduce any sugar), and when IB and I are present IB expresses. But when IA and IB are present together theyboth express their own types of sugars.
This is because of co-dominance. Hence red blood cells have both A and B types of sugars. Since there are three different alleles, there are six different combinations of these three alleles
that are possible, and therefore, a total of six different genotypes of the human ABO blood types.
1. The ploidy level of human being is :-
a. Haploidy b. Diploidy c.Triploidy d. Not certain
2. Which of the following gene is not produce sugar :-
a. IA b. IB c. IAIB d. i
3. how many types of sugars are found in red blood cells :-
a. A type sugar b. B type sugar
c. Both A& B type sugar d. A is rarely found and B is commonly found
4. How many alleles are responsible to determine blood group :- a. 2 b. 3 c. 4
d. 5
5. How many types of genotypes are found to make the human blood group :- a. 4 b. 5 c. 6 d. 7
Read the following Assertion and Reason based questions and select the most appropriate answer for the questions:-
a. Assertion and reason both are correct, and reason is correct explanation of the assertion.
b. Assertion and reason both are correct, and reason is not correct explanation of the assertion.
c. Assertion is correct and reason is incorrect.
d. Assertion is incorrect and reason is correct.
1. Assertion:- the point mutation is the substitution or replacement of a single nucleotide from DNA. Reason: - Sickle cell anemia caused due to point mutation.
2. Assertion: - Colour Blindness caused due to a recessive gene , which is found in X chromosome. Reason: - Colour blindness is an example of X linked Recessive
disease.
3. Assertion: - there are three pairs of alleles , which responsible to control the human skin colour. Reason: - The inheritance of human skin colour called as Polygenic
Inheritance.
4. Assertion :- The non disjunction of the homologous chromosome, is resulting as non proper distribution of the chromosomes. Reason :- Down‘s Syndrome disease is caused due to the non disjunction of the chromosomes.
5. Assertion :- There are triple alleles, IA , IB , i responsible to control the blood group of human being. Reason :- The controlling of one trait by number of alleles is called as multiple allelism.
6. Assertion :-when a pure red flowered and pure white flowered , dog flower plants are crossed together, pink flowered plants are produced in f-1 generation.
Reason :- this is the incomplete dominance , which create the pink colour of the flowers.
7. Assertion :- if the genotype is ―Tt‖, The phenotype of the pea plant is tall.
Reason :- Mendel‘s first law ― law of Dominance ― work to create phenotype in the heterozygous genotype.
8. Assertion :- The life span of Drosophila , is about 2 weeks. Reason:- for the linkage , T. H. Morgan selected , Drosophila as an experimental insect.
9. Assertion :- Alfred Sturtevant , used the frequency of recombination, to measure the distance between genes. Reason:- more frequency of recombination means , genes are located farther , low frequency of recombination means genes are located nearer.
10. Assertion :-In fowls , the female has ZW and male has ZZ sex chromosome.
Reason :- the sex determination in the fowls is done by the female, not by the male parent.
11. Assertion :- The male honey bees or the drones produced by parthenogenesis. Reason :- Male honey bees perform mitosis during
Gametogenesis.
12. Assertion :- In human female , XX is the sex chromosomal configuration. Reason :- The determination of the sex is done by both
the parents .
13. Assertion :- in phenylketonuria , phenyl alanine is excreted by help of urine. Reason :- Phenyl alanine has poor absorption , by the
kidney.
14. Assertion :- The possibility of a female becoming a haemophilic is extremely rare. Reason :- mother must be at least carrier and father must be
affected by the disease.
15. Assertion :- beta thalassemia , production of beta chain affected.
Reason:- it caused due to mutation in one or both genes on chromosome no. 16.
16. Assertion :- Chromosomal disorders can be classified into aneuploidy or polyploidy. Reason :- Chromosomal disorders can be caused either gaining of extra
copy number of chromosomes or an increase in a whole set of chromosome .
17. Assertion:- A male child can not be affected by colourblindness. Reason:-mother isa carrier for colour
blindness.
18. Assertion :- a female individual has rudimentary or non functional ovaries. Reason:- Strerility of the female caused due to the
Turner‘s Syndrome.
19. Assertion :- Genes and chromosomes have parallel behavior.
Reason :- Sutton & Boveri introduced chromosomal theory of inheritance to prove it.
20. Assertion :- The work of Mendel , remain , unrecognized till 1900.
Reason :- Expression of the traits , did not blend with each other , was not accepted by his contemporaries.
Study the following diagrams and give the answer of the following questions :
1. Which disease is represented in the karyotype :-
a. Turner‘s Syndrome b. Klinefelter‘s Syndrome
c. Down‘s Syndrome d. None of the above
2. Which pair of chromosome karyotype is representing the defect :-
a. 20th pair b. 21st pair c. 22nd pair d. 23rd pair
3. What is the term used for such triple chromosomal condition :-
a. Triploidy b. Trisomy c. Triple chromosomes d. All of the above
4. Select the most appropriate symptoms of the disease :-
a. Big andwrinkled tongue b. Broad flatface
c. Congenital heart disease d. All of the above
5. Why this condition appeared :-
a. Due to failure of segregation ofchromosomes
b. Due to Aneuploidy
c. Due to an additional chromosome
d. All of the above
Study the following diagram and answer the question :-
6. Mention the chromosomes in the male and female bird respectively :-
a. XY &XX
b. XO&XX
c. ZZ&ZW
d. ZW&ZZ
7. Which is the dominant trait of the position of flower:-
a. Terminal
b. Axial
c. Lateral
d. Sub terminal
8. Which amino acid found at sixth position :-
a. Glutamic Acid
b. Valine
c. Glysine
9. GUG codon is found in:
a. DNAb. t RNA
c. r RNA
d. m RNA
10. Which type of polypeptide is found at the end :-
a. HbA Polypeptide
b. HbS Polypeptide
c. Both A & B
d. Normal Polypeptide
11. Which type of disease , does the sickle cell anemia is :-3
a. Autosomal Recessive disorder
b. Autosomal Dominant Disorder
c. X linked Recessive Disorder
d. X linked Dominant Disorder
12. In the Hb(S) gene , which triple nucleotide , make codon GUG :-
a. GTG
b. CAC
c. Both A & B
d. None of the above






Comments
Post a Comment